Current Projects

Explainable Artificial Intelligence
While artificial intelligence algorithms can be used to solve problems that we find difficult, their solutions are often unintelligible to us. Artificial intelligence algorithms that can explain their solutions in a manner that humans can understand create new possibilities for both education and knowledge discovery.
Selected Papers:
Designing Children’s New Learning Partner: Collaborative Artificial Intelligence for Learning to Solve the Rubik’s Cube (2021)

Solving Combinatorial Puzzles with Deep Reinforcement Learning and Search
The Rubik's cube has over 10^19 possible configurations. We have created a deep reinforcement learning algorithm, called DeepCubeA, that can solve the Rubik's cube and 6 other combinatorial puzzles without domain specific knowledge. We are currently investigating how DeepCubeA can be used to solve problems in the natural sciences.
DeepCubeA Webserver
Selected Papers:
Solving the Rubik's Cube with Deep Reinforcement Learning and Search, Nature Machine Intelligence (2019)
Solving the Rubik's Cube with Approximate Policy Iteration, ICLR (2019)

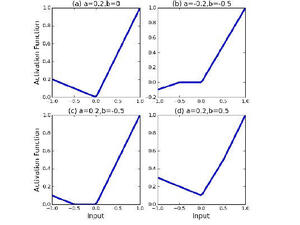
Learning Activation Functions
Artificial neural networks typically have a fixed, non-linear activation function at each neuron. We have designed a novel form of piecewise linear activation function that is learned though gradient descent. With this adaptive activation function, we are able to improve upon deep neural network architectures that use static activation functions.
Selected Papers:
SPLASH: Learnable Activation Functions for Improving Accuracy and Adversarial Robustness, Neural Networks, 2021
Learning Activation Functions to Improve Deep Neural Networks, ICLR Workshop, 2015

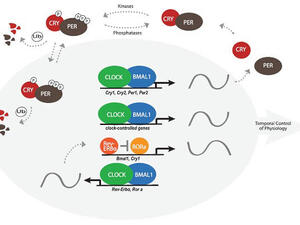
Circadian Rhythms
Circadian rhythms are found in virtually all forms of life. They play a fundamental role in functions ranging from metabolism to cognition. We have developed Circadiomics for accessing and mining circadian omic datasets and BIO_CYCLE for analyzing cicadian rhythms experiments using deep learning.
Circadiomics Webserver
BIO_CYCLE Webserver
Selected Papers:
CircadiOmics: Circadian Omic Web Portal, Nucleic Acids Research (2018)
What Time is It? Deep Learning Approaches for Circadian Rhythms, ISMB (2016)

The Hippocampus and Nonspatial Memory
The hippocampus plays a key role in the memory of sequences of events, however, the role of the hippocampus in nonspatial tasks has yet to be understood. Using unsupervised deep learning techniques, we visualize hippocampal activity during a nonspatial sequential memory task. We discovered that hippocampal activity correlates strongly with the sequence presented in this nonspatial memory task.
Selected Papers:
Hippocampal Ensembles Represent Sequential Relationships Among Discrete Nonspatial Events, BioRxiv (2019)